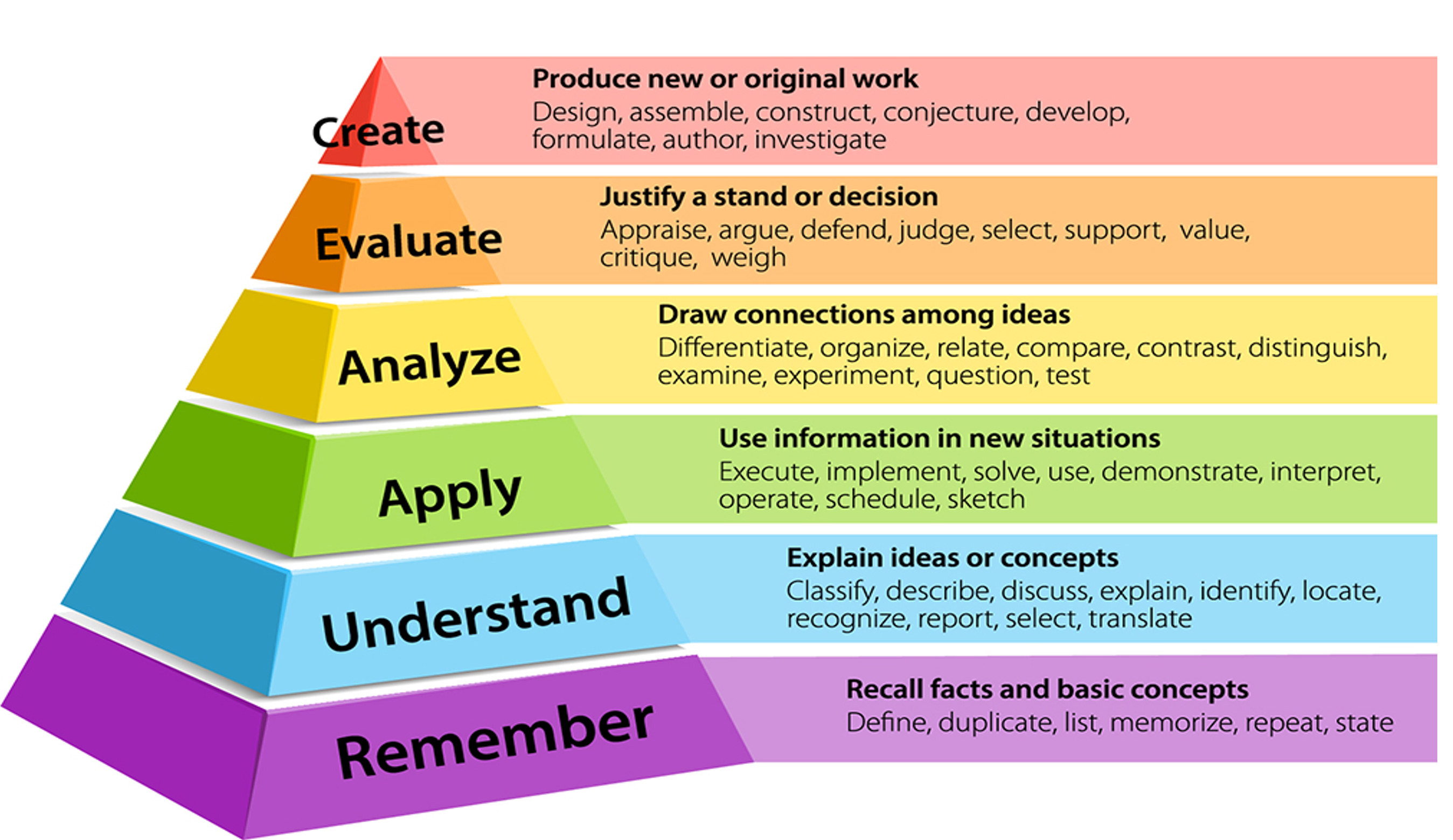
Bloom's Taxonomy
Wizard guides students through high levels within Bloom's taxonomy model for mastery-based learning.
The Theory of Fun for Game Design
Everything does not follow one, predictable pattern so Wizard embraces the theory of fun for game design:
- Drills are challenging and fun
- Users earn badges for achievements
- Gamification is incorporated into earning badges, and leads to engagement and participation
- Students can unlock games from a "Secret Game Stash" when progress thresholds are achieved
Metacognitive Theory
Wizard focuses students on their own learning and helps them think about what they do not yet know:
- Students are led efficiently through content - they do not need to spend time re-learning what they already know.
- Users earn badges for achievements.
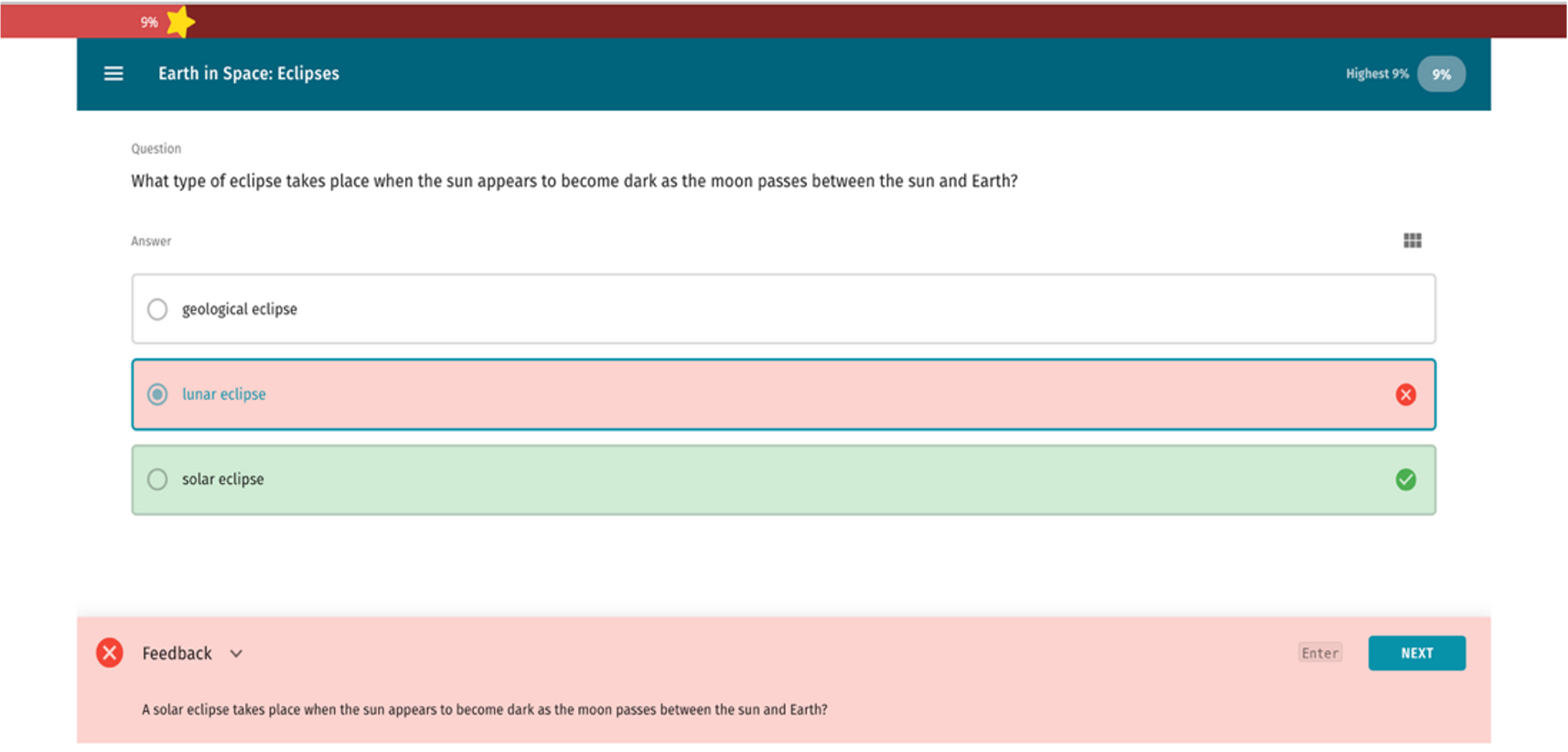
- Wizard provides immediate feedback so users can think about the WHY behind the concept.
- Students can use the progress bar to monitor their own progress to gain insight into their own learning.
The Theory of Deliberate Practice
Wizard ensures content mastery for long-term retention through focused practice that is purposeful and systematic:
- Immediate feedback helps a user learn from mistakes.
- Every child's pathway through Wizard will be different.
- Wizard adapts to what users have yet to master.
- Personalized, real-time pathway will be dependent on their incoming knowledge and learning capacity.
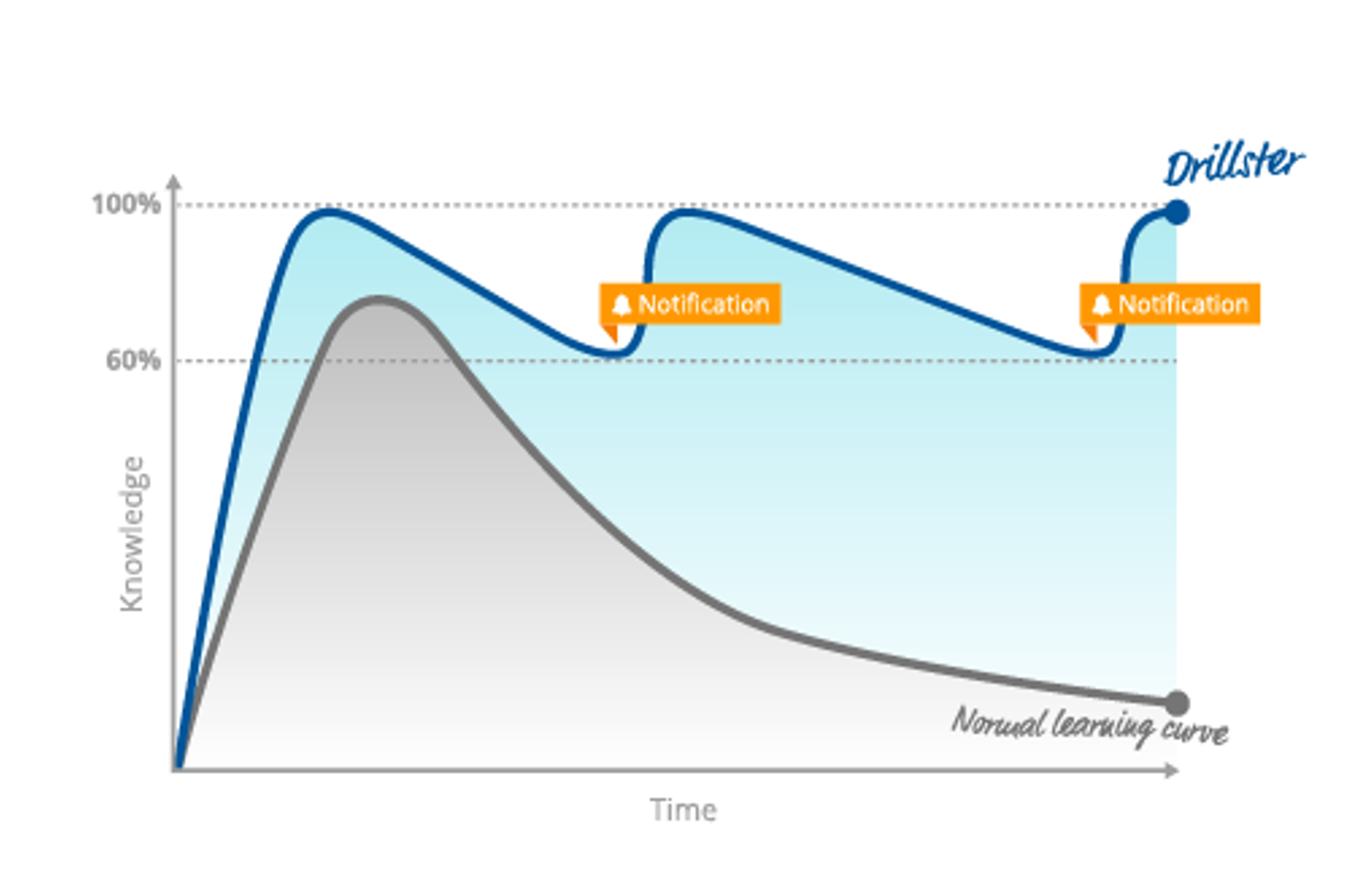
Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve
Wizard helps students retain information over longer periods of time by allowing continual practice. It knows where each student excelled and what was challenging for them to achieve mastery. We are bound to forget information over time if we do not revisit or practice:
- Wizard estimates each student’s mastery and teacher can prompt student to refresh their knowledge
- Wizard addresses memory decay
- Wizard reinforces long-term retention of curriculum information